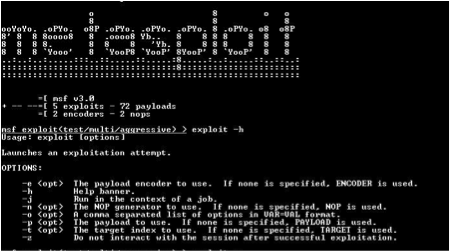
The
Metasploit Project is an
open-source computer security project which provides information about
security vulnerabilities and aids in
penetration testing and
IDS signature development. Its most well-known sub-project is the
Metasploit Framework, a tool for developing and executing
exploit code against a remote target machine. Other important sub-projects include the Opcode Database,
shellcode archive, and security research.
The Metasploit Project is also well-known for
anti-forensic and evasion tools, some of which are built into the Metasploit Framework.
Metasploit was created by
HD Moore in 2003 as a portable network tool using the
Perl scripting language. Later, the Metasploit Framework was then completely rewritten in the
Ruby programming language and has now become the world's largest Ruby project, with over 700,000 lines of code. It is most notable for releasing some of the most technically sophisticated
exploits to public
security vulnerabilities. In addition, it is a powerful tool for third-party security researchers to investigate potential vulnerabilities. On October 21, 2009 the Metasploit Project announced
[1] that it had been acquired by
Rapid7, a security company that provides unified vulnerability management solutions.
Like comparable commercial products such as Immunity's Canvas or Core Security Technologies'
Core Impact, Metasploit can be used to test the vulnerability of computer systems to protect them, and it can be used to break into remote systems. Like many information security tools, Metasploit can be used for both legitimate and unauthorized activities. Since the acquisition of the Metasploit Framework, Rapid7 has added two open-core proprietary editions called Metasploit Express and Metasploit Pro .